What's the difference between Oracle RAC and Oracle SE2HA?
Are you planning on upgrading to Oracle Database 19c? An upgrade to 19c provides your business access to Oracle premier support and an array of new features to help improve performance, enhance security, and expand functionality.
As you may or may not know, Oracle RAC no longer supports creating high-availability environments in Oracle 19c Standard Edition. Luckily there is a migration path to SE2HA that delivers similar high availability on Oracle Standard Edition.
In the following article, we define the characteristics of Oracle RAC and Oracle SE2HA and their differences to help you decide which option is right for your business. Let’s dive in!
What is Oracle SE2HA?
In Oracle 19c, SE2HA is the replacement of RAC on Standard Edition. Therefore, the use of SE2HA for failover can be set up without additional licensing.
Oracle SE2HA’s Architecture:
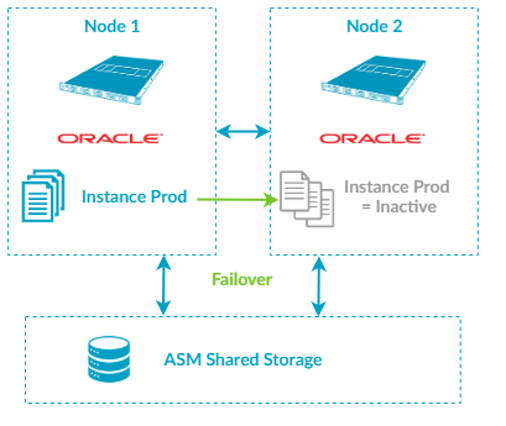
What are Oracle SE2HA's Characteristics?
1) Active (Running) Database Single Instance on One Node
The database is a single instance and can run up on one node at a time only. If the active node fails, the Oracle Grid will failover the SE2HA instance to the available passive node. The Oracle Grid then starts the instance on a passive node.
The Grid requires some time to do this, and the application won't reconnect immediately. In this case, you will need to be prepared for this when configuring your application.
2) The Oracle Grid Stack is Active at All Times on Both Nodes
The grid stack is active at all times on both nodes. The database instance is active/passive.
3) No Socket Limit Per Node
Although there is no socket limit per node on SE2HA (one socket limit per node on RAC), there is still the general limit for SE2, 16-threads. So, your SE2HA database can use a maximum of 16-threads instead of 32-threads when using both nodes in RAC.
4) Idle Node Does Not Require an Oracle License
While you can only use the hardware resources of just one node, the idle node does not require an Oracle license using the “10-day failover rule”. Check out this insightful blog by Oracle.
5) Not Required to Use Local Oracle Home On Each Node
Since an instance never runs on both nodes, you're no longer required to use local Oracle home on each node and store your database on ASM.
6) Extremely Easy Migration
Migrating to SE2HA is simple because SE2HA uses the same Oracle Grid stack as Oracle RAC and the grid configuration is the same as Oracle RAC.
What is Oracle RAC and what are Oracle RAC’s characteristics?
1) Oracle RAC has an Active (Running) Database Instance on Each Node
If either of the two nodes goes down, an active instance on the remaining node is immediately ready to accept any reconnect from the application. Users and applications will experience disconnection, but the reconnection should be instantly successful.
2) One-Socket Limitation Per Node
For RAC on SE2, there’s one socket limitation per node (unless using ODA).
3) 16-Thread Limit Per Instance
For SE2, on all types of instances (RAC, Single, SE2HA), a 16-thread limit per instance is imposed.
4) Utilize Hardware Resources of Both Nodes
You can connect an application to both nodes, so you're able to use hardware resources of both nodes - up to 32 threads (16-thread limit per instance) plus the memory of both servers.
It is advantageous for some applications and a downfall for others. The application needs to be designed with RAC in mind, or it can suffer performance issues when connected to two nodes.
5) Oracle Home is on Each Node Locally; Databases on Shared ASM Storage
It is common practice to have Oracle home locally on each node and databases on shared ASM storage.
Summarizing the Differences Between RAC and SE2HA
To help you decide between choosing RAC and SE2HA, we’ve created a high-level comparison below.
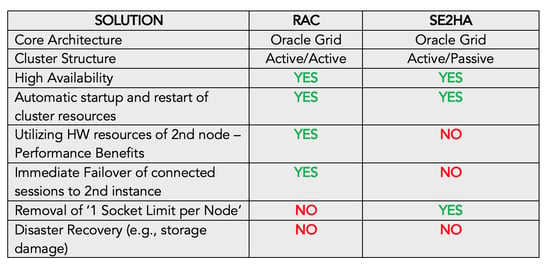
Oracle RAC and SE2HA both use the same Oracle Grid configuration. The difference is only in the database Oracle home and the database configuration itself.
From a high-level perspective, you can refer to SE2HA as an active/passive cluster and RAC as an active/active cluster.
For RAC, if either of the two nodes goes down, an active instance on the remaining node is immediately ready to accept any reconnect from the application. On the other hand, for SE2HA, the Oracle Grid starts the instance on a passive node, but the application will take a few minutes to reconnect.
You can retain the failover capability between nodes with SE2HA, although RAC’s performance benefits are no longer available because you cannot utilize the second node’s hardware. Something to note: there is no hardware limitation of ‘1 socket limit per node on RAC’ in SE2HA.
It is essential to note that neither RAC nor SE2HA offer disaster recovery functionality.
This licensing change by Oracle is in line with the EE and SE2 market segments - if you need performance, you're probably in need of EE and all of its features. Standard Edition (and SE2HA) still provides an excellent base for many companies, and the 16 threads should be more than adequate for most applications.
Determining Which is Better for Your Business: Oracle RAC or Oracle SE2HA
If you’re looking to create highly available environments, you have the option to decide between using the new SE2HA replacement or upgrading to Oracle Enterprise Edition.
Ultimately, whether SE2HA is right for you comes down to two key and simple questions:
a) Is 16 database threads (active sessions) for my application adequate?
b) Can I accept that my application will take a few minutes to reconnect to the passive node if the active node fails?
If you answered yes to these questions, SE2HA is a suitable RAC replacement for you.
Conclusion
To summarize in one sentence: SE2HA is a good RAC replacement for you if: (1) 16 database threads (active sessions) for your application is adequate and (2) the reconnection time for applications of a few minutes without data loss is also acceptable.
Does your organization have a plan in place if a disaster (power outage, human error, etc.) affects your shared storage or the entire facility? As you plan for your RAC upgrade path, we suggest taking the time to review your disaster recovery plan. A DR solution (such as StandbyMP) can provide fast failover (RTO), minimal data loss (RPO), and excellent resilience to all disasters.
In the next blog - Add Resilience to Oracle SE2HA (or RAC) Clusters with Disaster Recovery, we take you through the need and benefits of a DR solution and how you can expand your SE2HA cluster with DR functionality.
Journey to a High-Performance, Highly Resilient 19c Oracle SE Solution
Check out the rest of our blog series outlining the benefits of 19c, the upgrade path for RAC customers, and upgrade methods:
Subscribe to our monthly blog updates
By subscribing, you are agreeing to have your personal information managed in accordance with the terms of DBVisit's Privacy Policy
Tags: Oracle, SE2HA and DR, RAC










